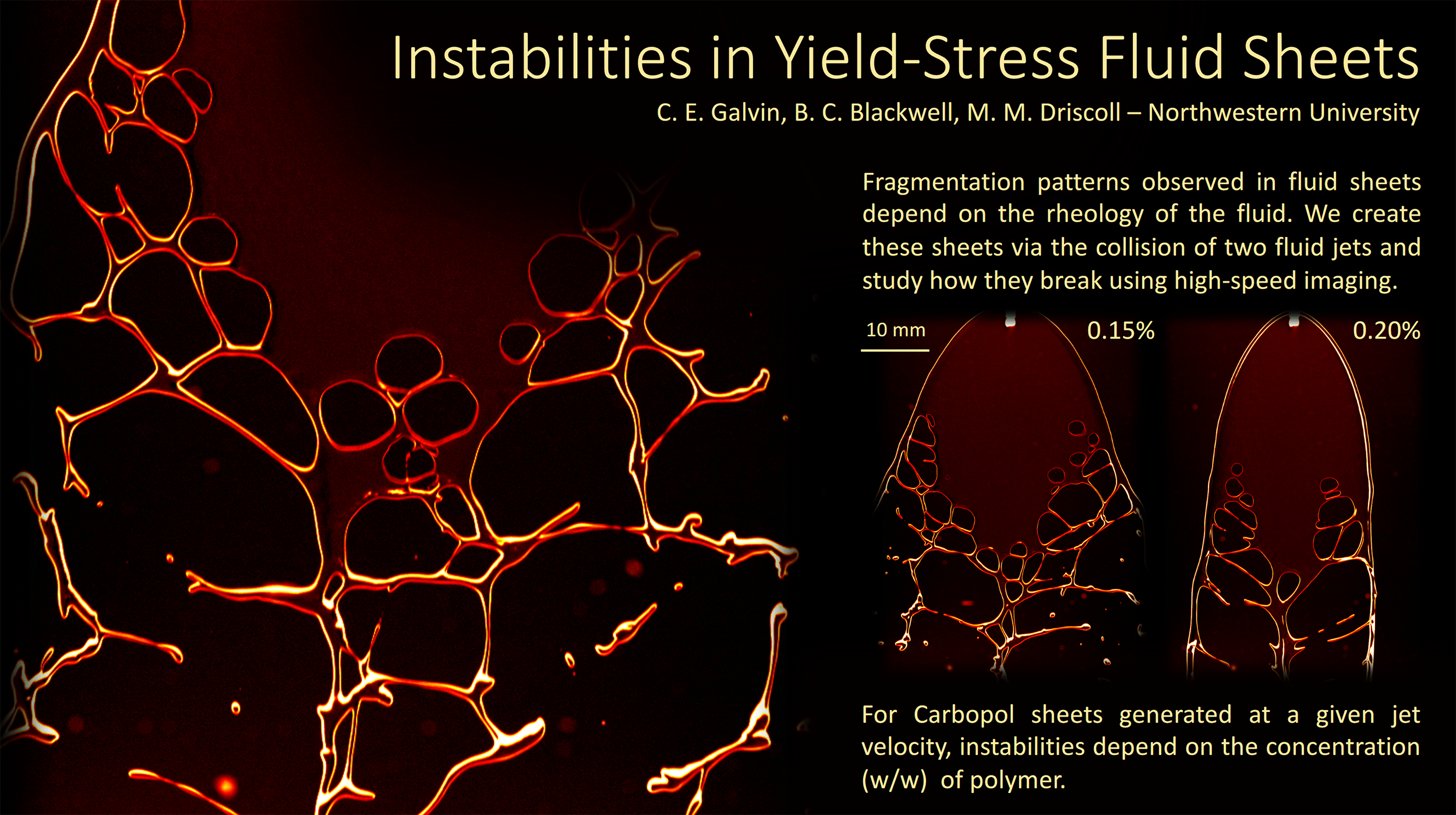
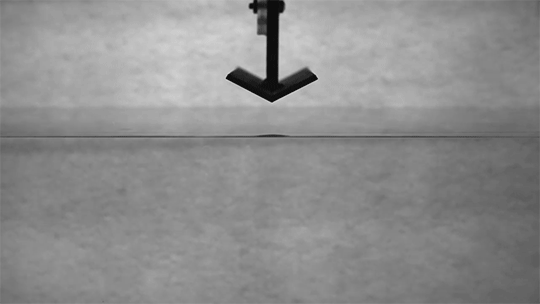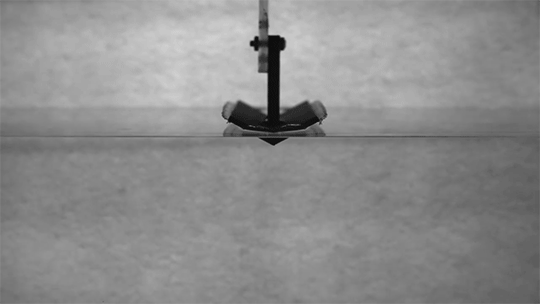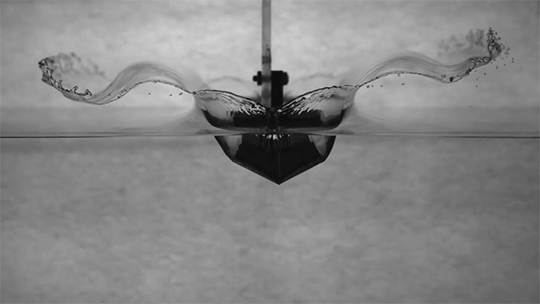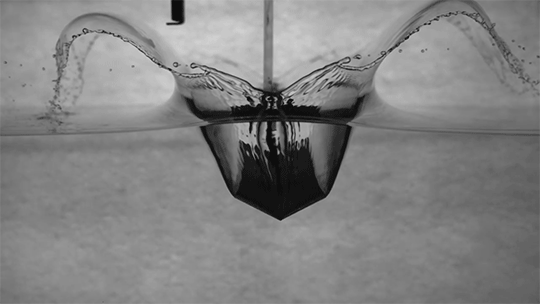
Even adding a small amount of polymers to a fluid can drastically change its behavior. Often polymer-doped fluids act more like soft solids, able to hold their shape like your toothpaste does when squeezed onto your toothpaste. Under a little stress, though, the fluids still flow; that’s why your toothpaste gets less viscous as you scrub.
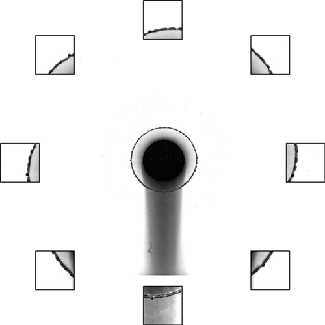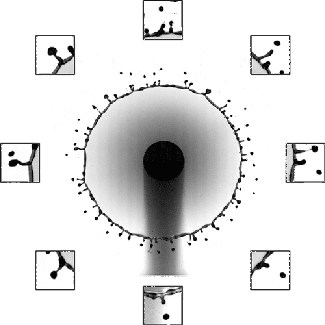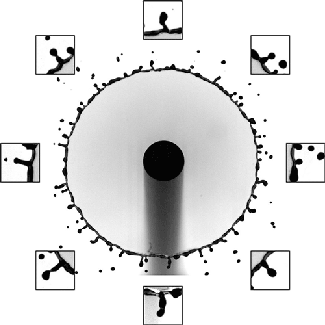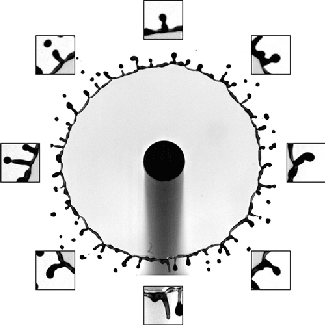
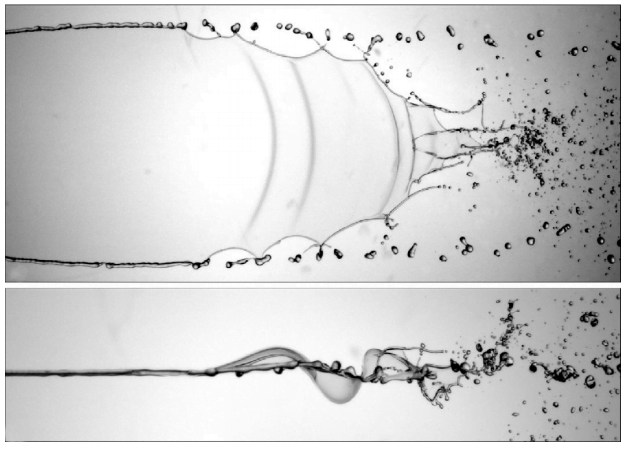
To study the changes polymers make, this research team collides two jets of fluid to create a liquid sheet. Depending on the flow rate and the added polymers, the break-up pattern of the sheet changes. By observing changes in the sheet thickness and the holes that form, they can draw conclusions about what the polymers are doing. (Video credit: C. Galvin et al.)