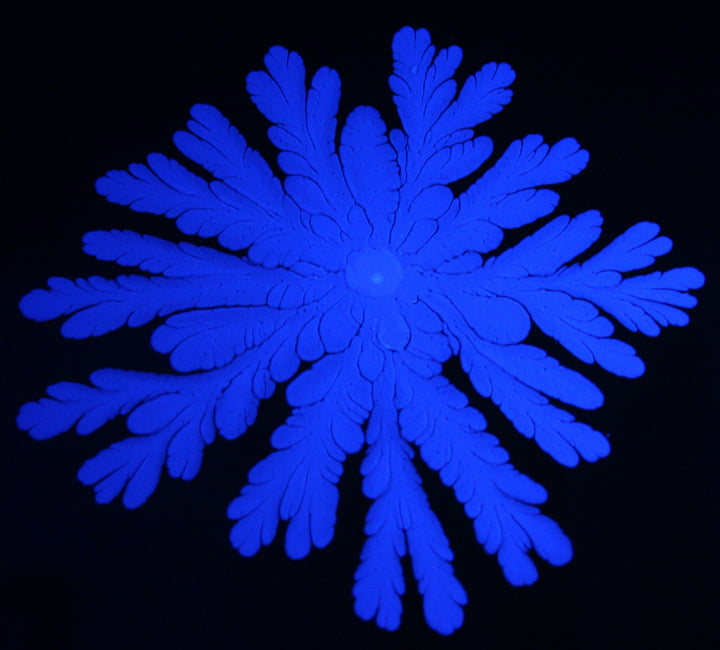
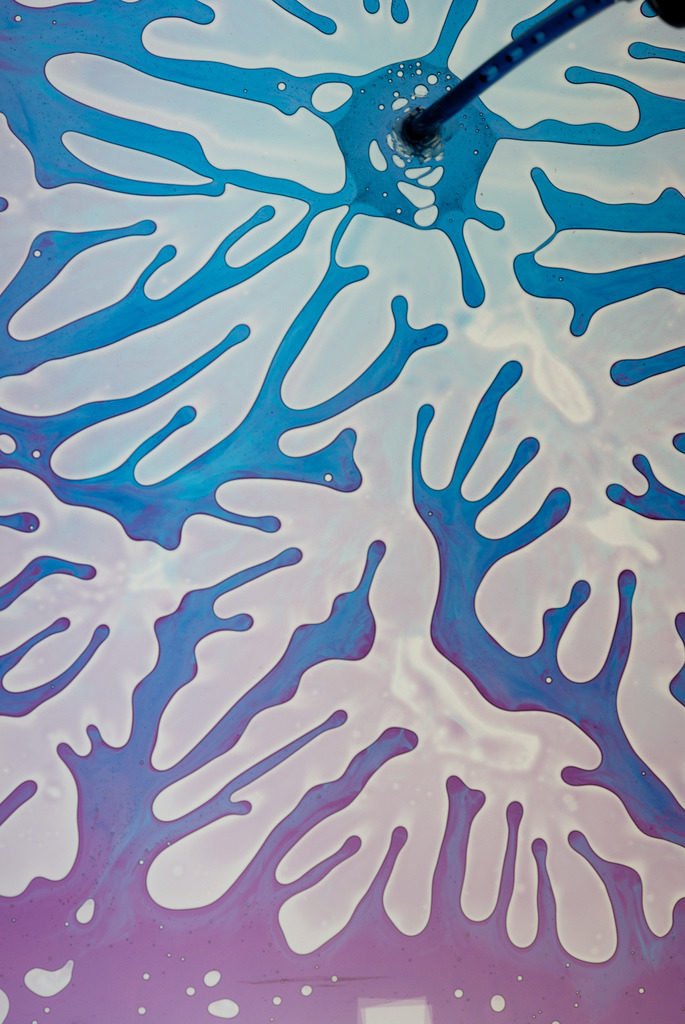
In this video, a thin film of viscous glycerin sits between two glass plates. As the plates are forced apart, air gets entrained from either side, causing finger-like instabilities to form between the two fluids. This is a result of the Saffman-Taylor mechanism. The final dendritic pattern depends on the fluid viscosities, surface tension, and any non-uniformities in the apparatus. (Video credit and submission by M. Goodman)
Tag: viscous fingering

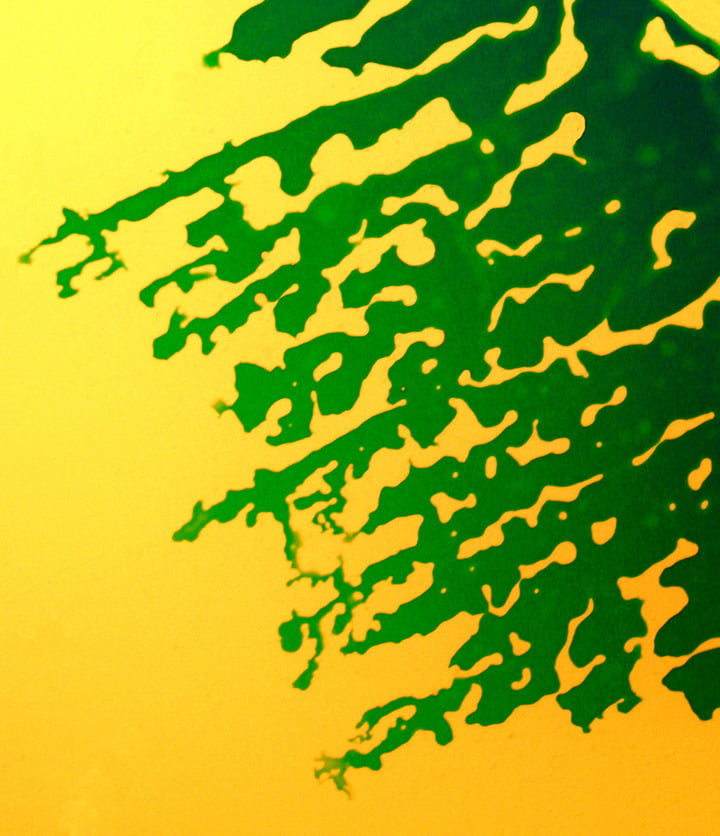
INK World v01
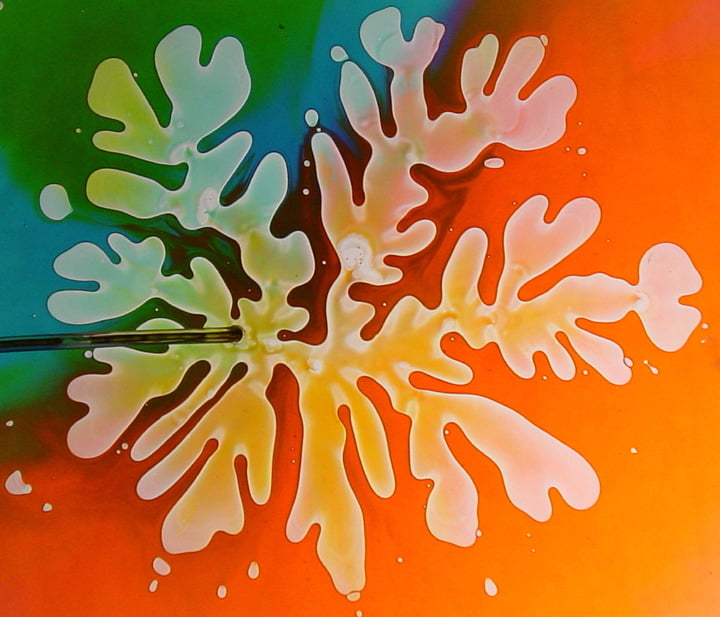
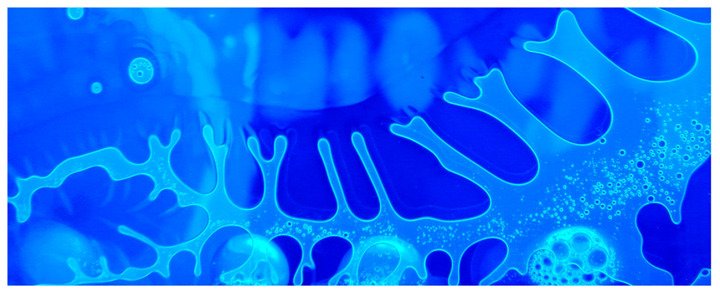
In this video, mixtures of inks (likely printer toners) and fluids move and swirl. Magnetic fields contort the ferrofluidic ink and make it dance, while less viscous fluids spread into their surroundings via finger-like protuberances. (Video credit and submission: Antoine Delach)

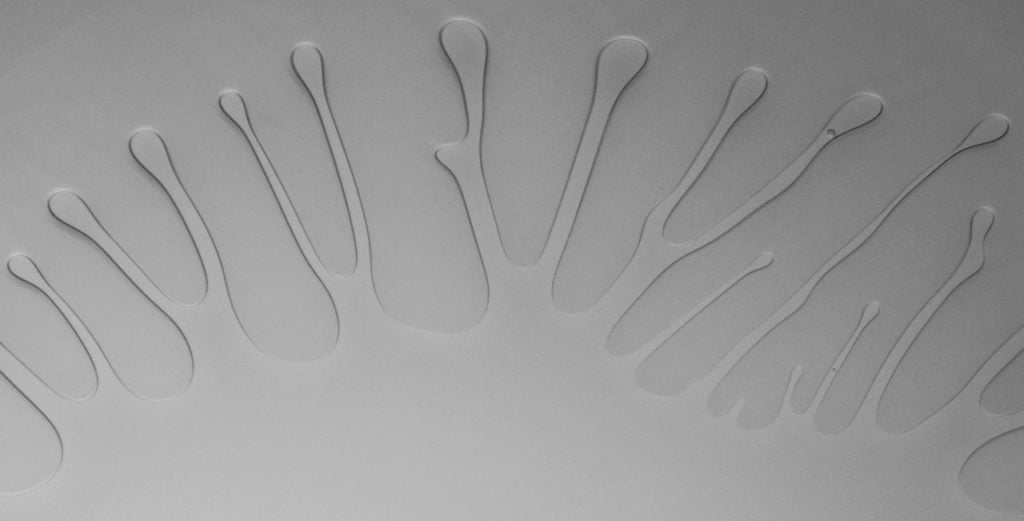
Viscous Fingers
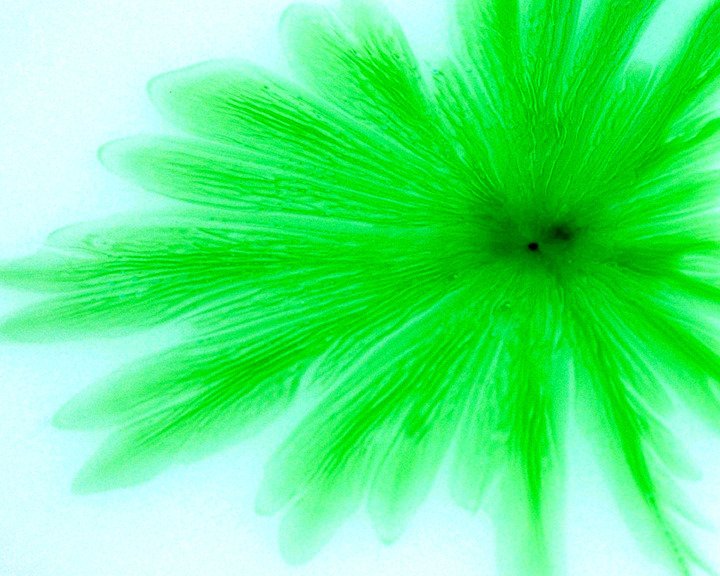
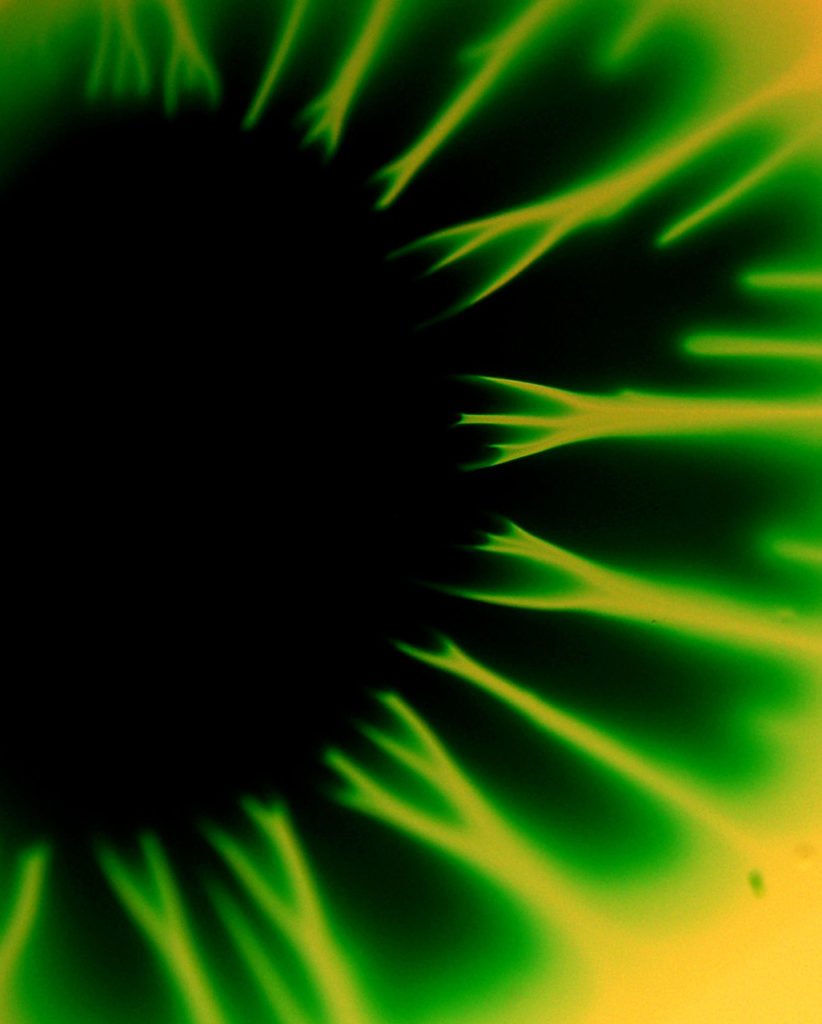
High viscosity silicon oil is sandwiched between two circular plates. As the upper plate is lifted at a constant speed, air flows in from the sides. The initially circular interface develops finger-like instabilities, due to the Saffman-Taylor mechanism, as the air penetrates. Eventually the fluid will completely detach from one plate. (Photo credit: D. Derks, M. Shelley, A. Lindner)

Flow Vis
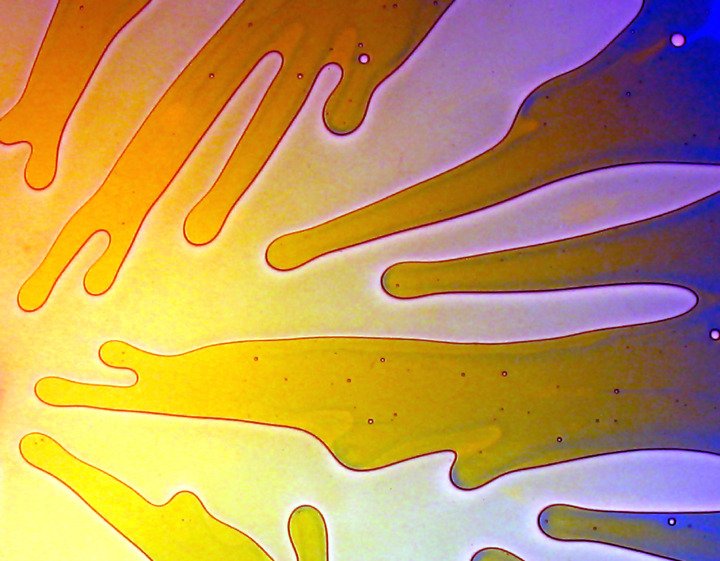
Place a viscous fluid in the gap between two plates of glass and you have created a Hele Shaw cell. If a less viscous fluid is then injected between the plates, a fascinating pattern of finger-like protrusions results. This is known as the Saffman-Taylor instability. Because of the relative simplicity of the set-up, it’s possible to create such experiments at home using common household fluids like glycerin, dish soap, dyed water, or laundry detergent. (Photo credits: Jessica Rosencranz, Jessica Todd, Laurel Swift et al, Andrea Fabri et al, Tanner Ladtkow et al, Mike Demmons et al, Trisha Harrison, Justin Cohee, and Erik Hansen)

Viscous Fingers
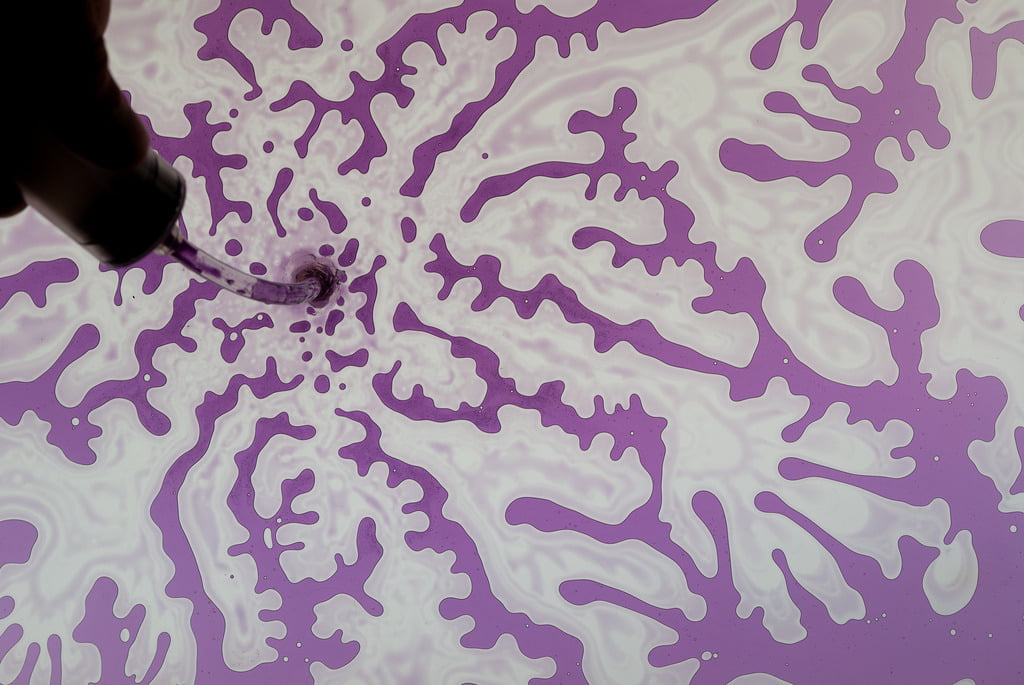
The Saffman-Taylor instability occurs when a less viscous fluid is injected into a more viscous one, usually in a Hele-Shaw cell. Here oil paint and mineral spirits were painted onto flat surfaces that were pressed together before being pulled apart. The result is viscous fingering of the fluids. #