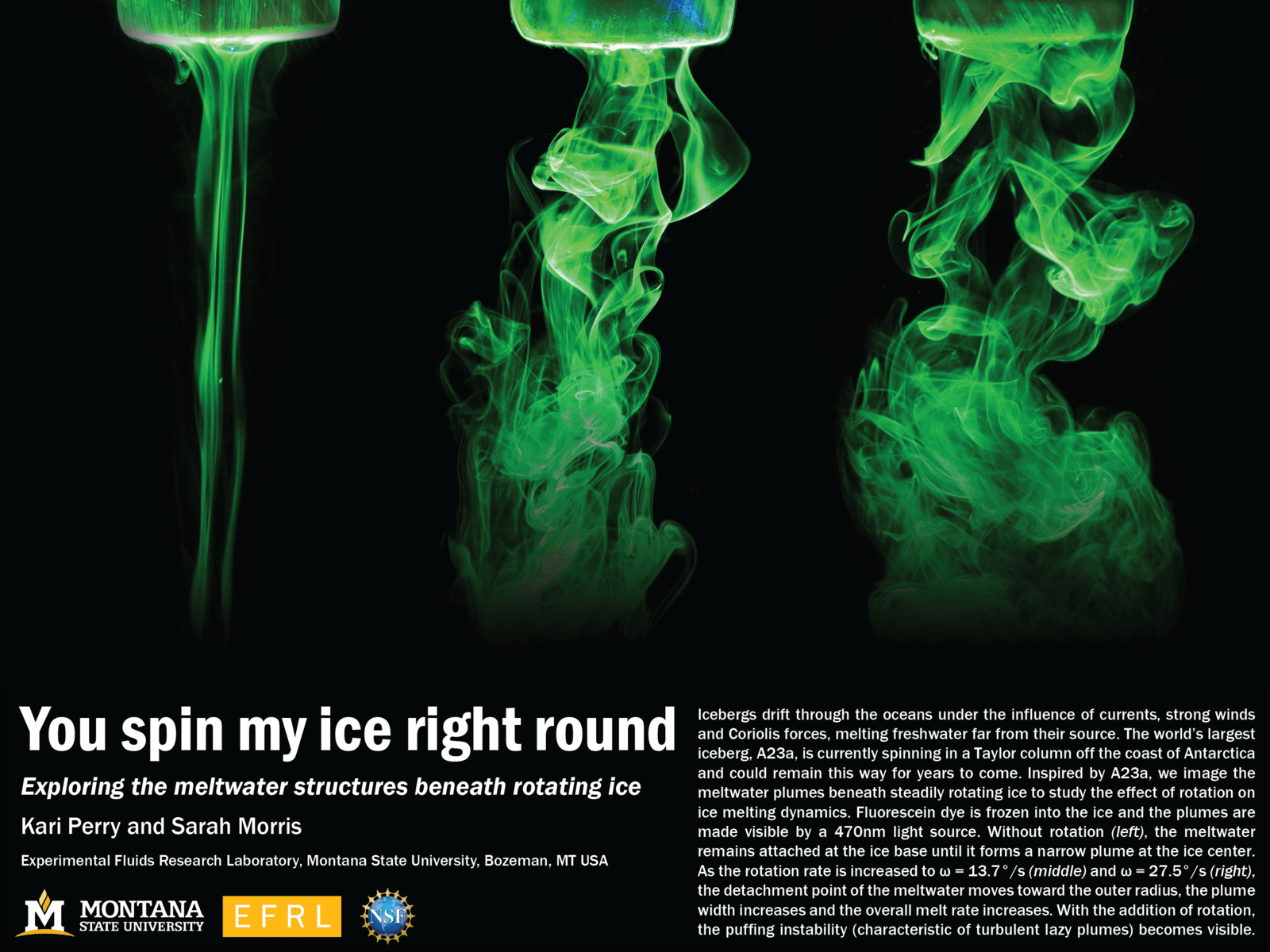
The world’s largest iceberg A23a is spinning in a Taylor column off the Antarctic coast. This poster looks at a miniature version of the problem with a fluorescein-dyed ice slab slowly melting in water. On the left, the model iceberg is melting without rotating. The melt water stays close to the base until it forms a narrow, sinking plume. In the center, the ice rotates, which moves the detachment point outward. The wider plume is turbulent compared to the narrow, non-rotating one. At higher rotation speeds (right), the plume is even wider and more turbulent, causing the fastest melting rate. (Image credit: K. Perry and S. Morris)
Tag: 2024gfm

How CO2 Gets Into the Ocean
Our oceans absorb large amounts of atmospheric carbon dioxide. Liquid water is quite good at dissolving carbon dioxide gas, which is why we have seltzer, beer, sodas, and other carbonated drinks. The larger the surface area between the atmosphere and the ocean, the more quickly carbon dioxide gets dissolved. So breaking waves — which trap lots of bubbles — are a major factor in this carbon exchange.
This video shows off numerical simulations exploring how breaking waves and bubbly turbulence affect carbon getting into the ocean. The visualizations are gorgeous, and you can follow the problem from the large-scale (breaking waves) all the way down to the smallest scales (bubbles coalescing). (Video and image credit: S. Pirozzoli et al.)